Kyrgyzstan 2012 "Prehistoric animals"
| <prev | back to index | next> |
| Issue Date | 08.12.2012 |
| ID | Michel: 726-729 (A - perforate, B - imperforate ); Scott: 422-425; Stanley Gibbons: 521-524; Yvert et Tellier: 602-605; Category: pR |
| Design | Eldiyar Isakov |
| Stamps in set | 4 |
| Value |
S23 - Kyrgyzsayrus S30 - Xenacanthidae S40 - Longisquama insignis S52 - Mammuthus |
| Emission/Type | commemorative |
| Issue place | Bishkek |
| Size (width x height) | 40x28mm |
| Layout | 4 Sheets of 6 stamps each |
| Products | FDC x1 |
| Paper | chalky |
| Perforation | 14.25x14 |
| Print Technique | offset |
| Printed by | Publishing house "Belarusian Printing House", Belarus |
| Quantity | perforate: 6.000 sets (1.000 sheets) imperforate: 1.500 sets (250 sheets) |
| Issuing Authority | Ministry of Transport & Communication Kyrgyz Rep |

On December 8th, 2012, the Post Authority of Kyrgyzstan issued a set of four stamps - "Prehistoric animals", that shows prehistoric animals who lived on territory of the country at various points in geologic time from the Triassic to the Quaternary periods.
Note: Similar stamps exist that are imperforate.
Fossils of all these animals are found in Madygen Formation in Kyrgyzstan.
The territory of Kyrgyzstan along with China, Mongolia, Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan is a haven for paleontological research. In the Jurassic Period, 160 million years ago, these areas were inhabited by various prehistoric animals. During USSR times, Soviet paleontologists found numerous remains of prehistoric animals and fish in southern Kyrgyzstan Madygen Formation. These fossils can be seen at the Paleontologic Museum of Moscow.
Kyrgyzsaurus is an extinct genus of drepanosaurid archosauromorph known from the Triassic of southwestern Kyrgyzstan.
 |
| Kyrgyzsaurus on stamp of Kyrgyzstan 2012 MiNr.: 726, Scott: 422. |
 |
| Xenacanthidae on stamp of Kyrgyzstan 2012 MiNr.: 727, Scott: 423. |
Longisquama is an extinct genus of lizard-like reptile from Late Triassic (about 200 million years ago).
 |
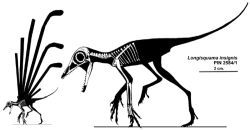 |
| Longisquama on stamp of Kyrgyzstan 2012 MiNr.: 728, Scott: 424. | Longisquama's reconstruction. Image credit: Wikimedia |
This is undoubtedly one of the most amazing animals. Small size, about 15 centimeters lizard along the back which protruded two rows of long feather scales. The length of these scales is as long as the length of the animal. Longisquama used them instead of a parachute. Jumping down from the tree, she unfolded a fan of scales and slowly lowered to the ground similar to a shuttlecock from badminton. It was one of the first attempts for vertebrates to fly. There were no other animals that could fly except for insects. Perhaps insects were the diet of Longisquama, who preyed it by jumping down from the trees.
Mammuthus - an extinct genus of mammal elephant's family, who lived during the Quaternary Period (2.6 million years ago to the present).
 |
| Mammuthus on stamp of Kyrgyzstan 2012 MiNr.: 729, Scott: 425. |
Products and associated philatelic items
| FDC | First-Day-of-Issue Postmark | Example of circulated covers |
 |
 |
 |
| The reverse side of the FDC contains technical details about the issue. | ||
| Mini-Sheets with perforate and imperforate stamps | ||
 |
 |
|
References

|
The Department of Postal Products (Kyrgyzmarkasy): [1], [2], [3], [4];
diesel.elcat.kg (forum); colnect; Ukrafil; Evening Bishkek (the article doesn't exist anymore).
Acknowledgements
Many thanks to Dr. Peter Voice from Department of Geological and Environmental Sciences, Western Michigan University, for review of a draft of this article.| <prev | back to index | next> |